search
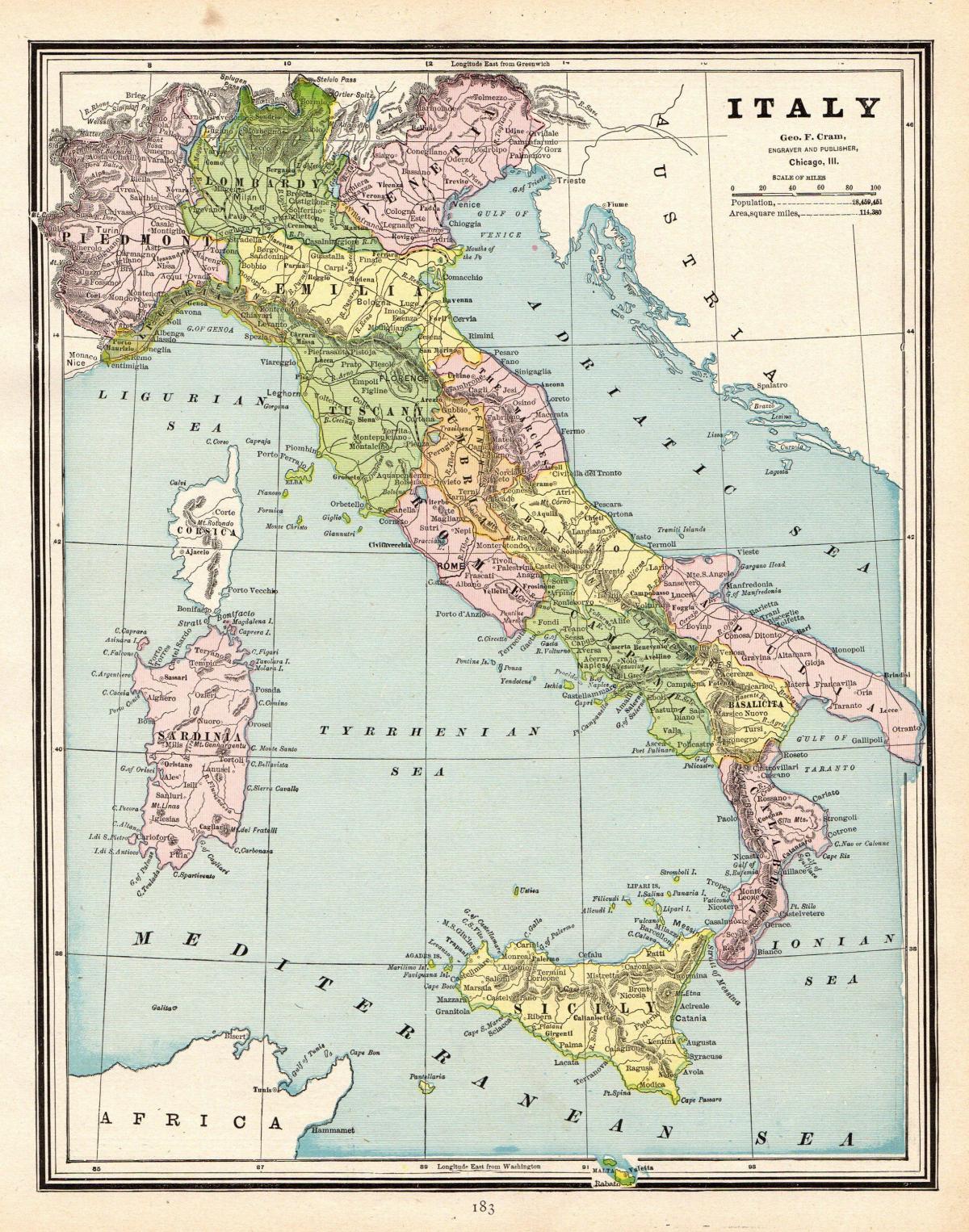
Vintage map of Italy
Map of Italy vintage. Vintage map of Italy (Southern Europe - Europe) to print. Vintage map of Italy (Southern Europe - Europe) to download. The Etruscan civilization flourished in central Italy after 800 BC. The origins of the Etruscans are lost in prehistory. The main hypotheses are that they are indigenous, probably stemming from the Villanovan culture, or that they are the result of invasion from the north or the Near East as its shown in the vintage map of Italy. A more recent study has suggested a Near Eastern origin. The researchers conclude that their data, taken from the modern Tuscan population, 'support the scenario of a post-Neolithic genetic input from the Near East to the present-day population of Tuscany’. In the absence of any dating evidence there is however no direct link between this genetic input and the Etruscans.
Many of the new Hellenic cities became very rich and powerful, like Neapolis (Νεάπολις, Naples, "New City"), Syracuse, Acragas, and Sybaris (Σύβαρις) as you can see in the vintage map of Italy. Other cities in Magna Graecia included Tarentum (Τάρας), Epizephyrian Locri (Λοκροί Ἐπιζεφύριοι), Rhegium (Ῥήγιον), Croton (Κρότων), Thurii (Θούριοι), Elea (Ἐλέα), Nola (Νῶλα), Ancona (Ἀγκών), Syessa (Σύεσσα), Bari (Βάριον), and others. After Pyrrhus of Epirus failed in his attempt to stop the spread of Roman hegemony in 282 BC, the south fell under Roman domination and remained in such a position well into the barbarian invasions (the Gladiator War is a notable suspension of imperial control). It was held by the Byzantine Empire after the fall of Rome in the West and even the Lombards failed to consolidate it, though the centre of the south was theirs from Zotto conquest in the final quarter of the 6th century.
Etruscan expansion was focused accros the Apennines. Some small towns in the 6th century BC have disappeared during this time, ostensibly consumed by greater, more powerful neighbors. However, there exists no doubt that the political structure of the Etruscan culture was similar, albeit more aristocratic, to Magna Graecia in the south as its shown in the vintage map of Italy. The mining and commerce of metal, especially copper and iron, led to an enrichment of the Etruscans and to the expansion of their influence in the Italian peninsula and the western Mediterranean sea. Here their interests collided with those of the Greeks, especially in the 6th century BC, when Phoceans of Italy founded colonies along the coast of France, Catalonia and Corsica. This led the Etruscans to ally themselves with the Carthaginians, whose interests also collided with the Greeks.